Duplicate content is one of the most common glitches your page might be experiencing. Google once stated that duplicate content is unavoidable on the internet. They don’t really penalize websites for having such content, just as long as it’s not done in an abusive or malicious way.
Some of us might still be wondering how Google really handles this issue. If you’re someone using digital marketing in the Philippines and wants to know how Google treats duplicates, I suggest you watch this short video by Google Webmasters. Here, they answer the question “How does Google handle duplicate content?”
A website could have duplicate content because of several reasons – they are mostly technical. It’s important to know the ups and downs of your own website even if you already have a web developer who handles everything. However, if you’re a solopreneur who does all the SEO on your own, this blog can be a great guide for you.
Duplicate Content: Why does it happen and how can you get rid of it
The most common reason for on-page content duplication is URL variations. These specific problems may cause negative impacts on your website’s rankings:
- URL variations caused by auto-archiving
- Identical titles and meta description due to pagination
- Different URL parameters (also known as query string)
- Printer-friendly pages
- Content syndication
Allow me to explain further.
URL variations caused by auto-archiving
The easiest way to determine if your website has archived pages is to type in site:example.com on the Google search bar replacing the word example with the name of your website.
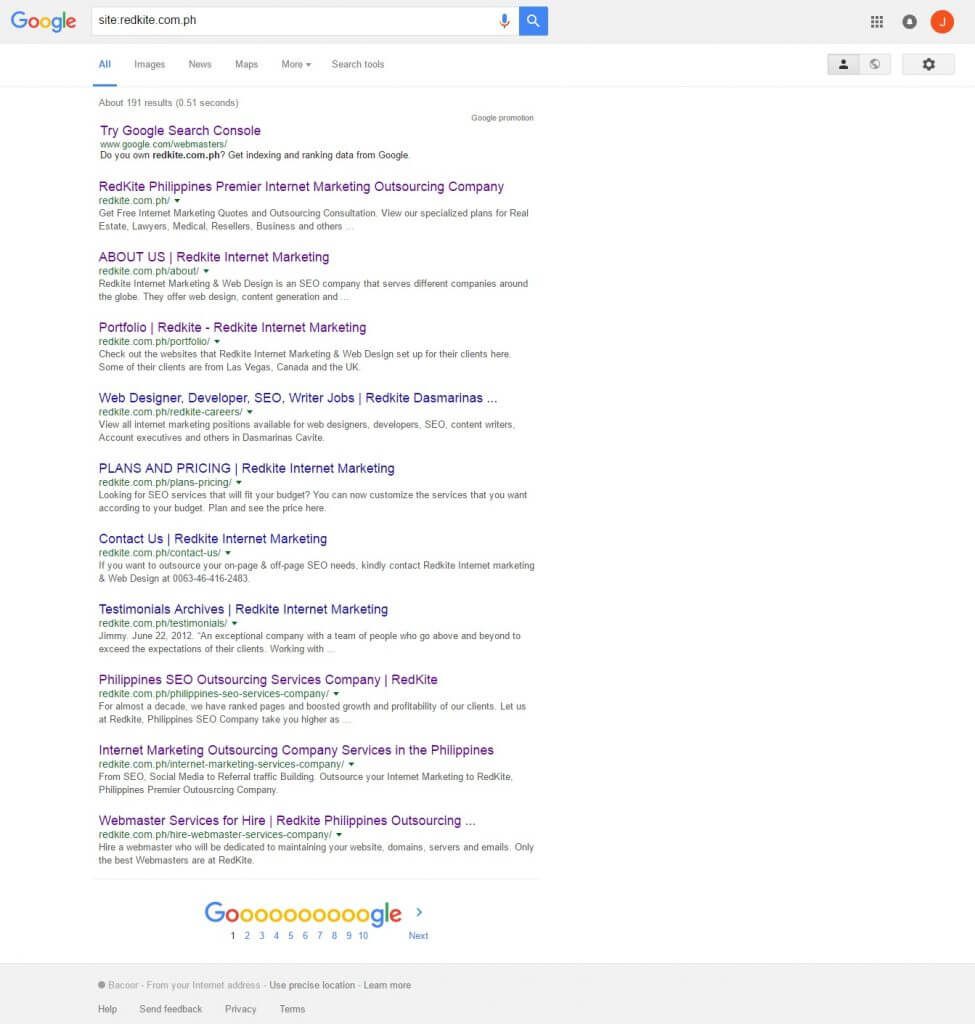
You’ll see the number of generated results from Google on the upper part. The displayed pages are normally the ones the system thinks are the most relevant.
To see the pages with duplicate content, go to the very last page and at the bottom part, you’ll see this:
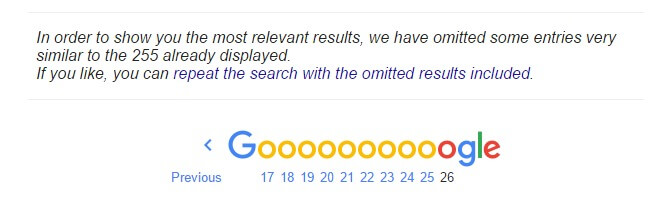
Click the link to see all your archived pages.
This problem is common among websites that use WordPress as their Content Management System (CMS). It is because WordPress has a feature that allows readers to choose from a variety of ways on how they prefer to browse content – by date, by category, by tag or by author.
As convenient as it is for your page visitors, Google bots fail to distinguish what these pages are for. This is when different URL variations happen.
The solution to this problem is quite simple. All you have to do is to let Google know which pages do not need indexing. Hence, the Meta tag you will need is “follow, no-index.” In WordPress, you can make use of the handy plugin WordPress SEO by Yoast so that you will be able to automatically add the Meta tags to the pages that don’t need indexing.
Identical titles and Meta description due to paginations
Pagination is the sequential numbering of related pages in a website. Normally, when a content gets too long or too many, webmasters opt to divide them into different pages. I’m sure this is something you would also do given the circumstances that you have lengthy content.
Pagination is widely used in all types of websites including E-Commerce, blog sites such as WordPress, and even Google itself.
You might be wondering, “So why is this a problem?”
If you look at it from an SEO point-of-view, this can cause serious issues the moment Google tries to index your website’s content. One of these problems include duplicate content.
Duplicate content caused by pagination still depends on how a website lays out information. However, it is almost unavoidable not to have identical content since some elements displayed are actually the same.
Take E-Commerce websites as an example. This type of website normally practices pagination because of the wide range of products it offers to its potential customers. This is mostly evident with real estate websites that offer multiple properties in specific locations. The identical title keys and Meta descriptions tend to propagate the span of the paginated content. This causes confusion to the Google bots when they need to show results for certain search queries which relate to your website’s content.
The more paginated your content is, the less link juice (or Page Rank) it gets. Which means it’s more difficult it is to be crawled and indexed. So how do you deal with this? It’s actually quite simple and there are several ways to solve it.
Option #1
The first remedy you can try is similar to the solution for archived pages – the “Follow, no Index” Meta tag.
There are situations wherein it’s not really necessary to make certain pages searchable on the Google SERPs. When you opt to use this Meta tag, you’re allowing the page authority to point back to the first page of the paginated series. This is actually the least complicated among all the possible solutions for duplicate content.
Option #2
The next option you have is to make a separate view all page. This is a page that displays all the items within a single page. By doing this, the search engines will recognize the view all page as the original page to index. You can apply this if you are using WordPress as your CMS. Refer to the image below to see where you can find the option to put the canonical URL of a page.
When you add a new post on WordPress, you’ll be redirected to the section where you will be able to input a blog. Directly below that, you will see this:
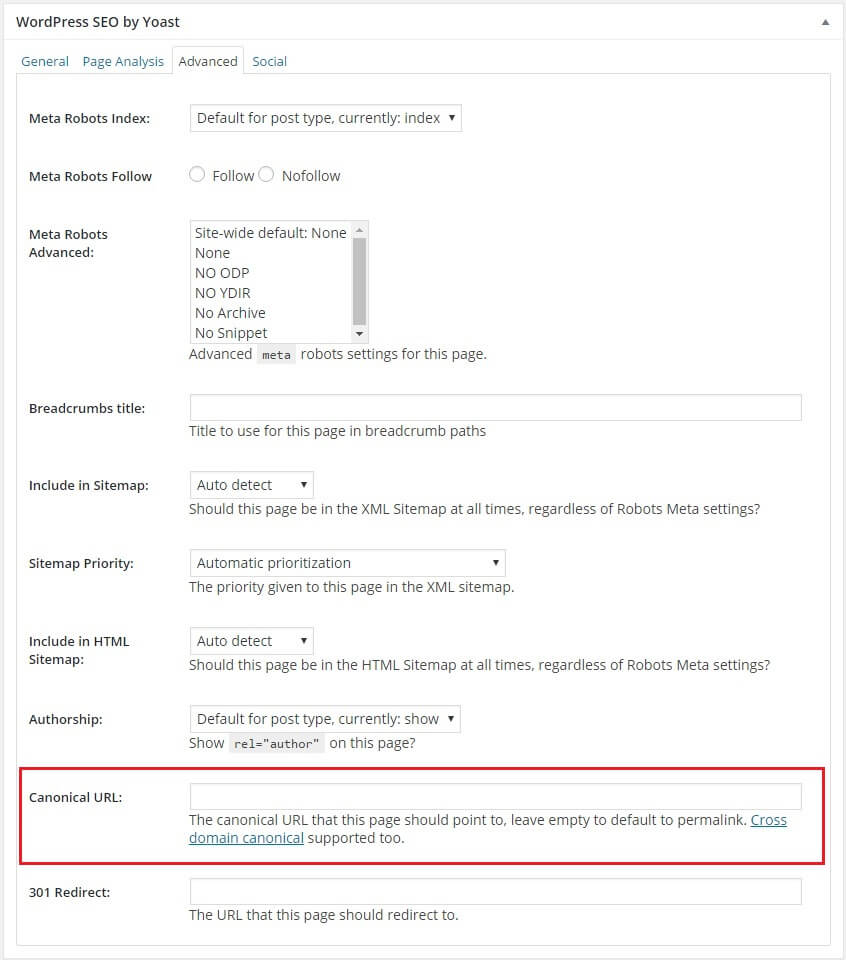
However, if you are using a different CMS for your website that doesn’t have a quick option similar to the one above, you can add the adjustments on the database of your site by placing the tag within the <head> section of the paginated content and link to the view all page.
By doing this, you are basically telling Google to treat each page included in the paginated series as a segment of the view all page, making search queries point directly to that page whenever it applies.
This option is relatively simple but does not really fit well if the website’s content includes articles with large images or product listings with hundreds of pages.
You should also consider page load speed if you are going for this kind of solution. Just like in any other type of business, all our customers would always prefer fast service and this also applies when potential clients browse our websites. If the page takes too long to show results, there is a big chance our page visitors will click the back button and go to the next website on their list.
Option #3
This last option can be the most complicated method, but it may also be the best one to choose because of its versatility.
The Meta tag you will be using here is the rel=”prev” and “next” HTML attributes. Using this will help you indicate if a certain page belongs to a sequence of paginated content. Doing this method may be a bit tedious, especially if there are a lot of sequenced pages.
Technically, you’re creating a chain between all the pages with related content if you choose this method for your website’s pagination series. If you want to learn more about this, then I suggest you read through this Google Webmaster Central blog.
Different URL parameters
Another issue that causes duplicate content is the different URL parameters – also known as query string. A query string is the text seen at the end of a URL, normally after the “?” character. See example below:

There are several instances wherein a website uses a query string:
- A search feature is present on the website to help page visitors look for specific content.
- There is pagination in the website.
- Submission of forms is involved.
- There is sorting of specific lists.
Observe the URL of the example image shown above. The query string it displays says “?sort=20a&page=1” because it is the first page of a paginated content. This is what the URL will show when you select a different page:

Another example is the query string caused by an onsite search bar. See image example below:
![]()
I typed in the word steroids in the search bar of the website and it redirected me to this page:
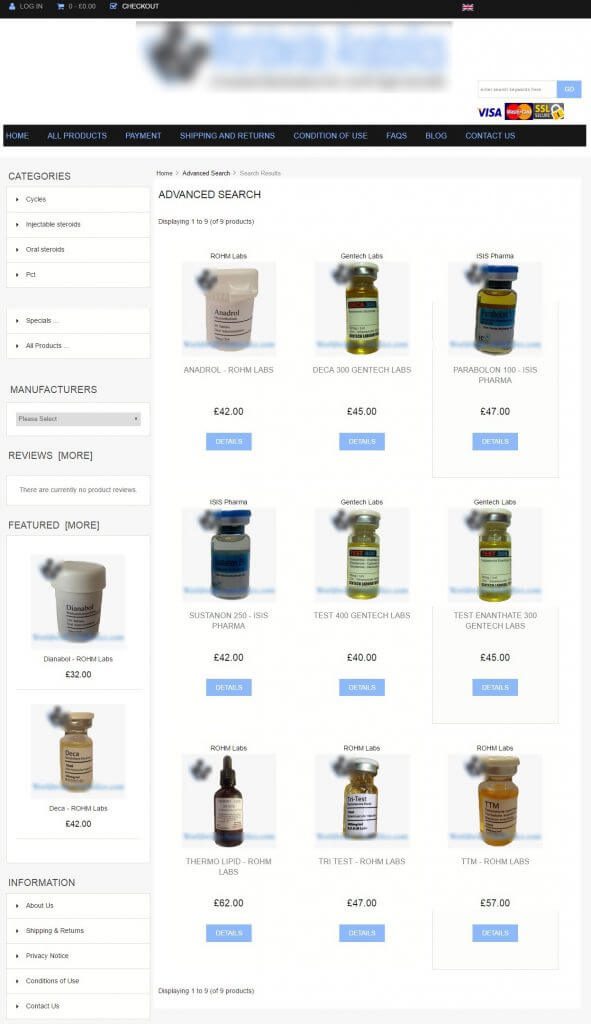
When you enter a specific search query in the search bar of a website, the page will generate a new URL depending on what you are looking for.
As convenient as it is to have these kind of features on a website (especially among pages that need to have paginated content and an on-page search bar to ensure quality user experience similar to the example above), keep in mind that it can also be a major cause of duplicated content if things are not handled properly.
Refer again to the last image shown above. When I looked for the keyword “steroids,” the advanced search displayed those results.
Since I searched for a specific product, the website displayed the items that fall under the category of what I was looking for. If a website is not properly coded, chances are this will cause content duplication due to similar URLs with different parameters.
The quick fix for this problem is to use the canonical tag on a page to let Google know which version needs indexing. Doing so will redirect all the page rank on the original version when searching a particular query and this can increase authority as well as the rank of this page on the Google SERPs.
Printer-friendly pages
Most websites we see today contain too much images and ads and this makes it difficult for web browsers to print content directly from a website. This is why most websites now feature a printer-friendly version of every page.
This is a good thing for the browsers, but something to be cautious of if you look at it from an SEO perspective. Having printer-friendly pages has high probability of causing duplicate content because of pretty obvious reasons. However, there are two simple ways to resolve this:
First is by using the canonical tag, which I already discussed several times above.
Second is by implementing the /robots.txt file, which is similar to the concept of the No Index, No follow tag. Using this will instruct the web crawlers that they should not visit the page that has this kind of setting. This is commonly refereed to as The Robots Exclusion Protocol.
Content Syndication
There are two way to view content syndication:
It can be a positive thing for your website when you allow your content syndication because it will be able to reach a wider range of audience, especially if the website that wants to use your content has higher authority than your site.
However, when content syndication is not properly handled, it can cause duplicate content.
There are several ways to deal with this problem:
First is by using the handy canonical tag; second is by implementing the No Index tag; and lastly is the direct attribution link.
We already discussed several times earlier how canonical and no index tags works. When you allow content syndication, it is best to use either of the first two options. However, if the website that wants to use your content would rather opt for the third best choice, make sure to get a link directly from the syndicated content to your original post and not to your website’s homepage.
Remember that Google bots don’t always get things right and when you have this kind of link, your content might be mistaken for a duplicate and this can pull your site rankings down.
Duplicate Content: What’s the best tool to use when looking for it
There are several tools you can use in checking your website for duplicate content. You can use the Google Webmasters Tools and Google search, but the best tool I would personally recommend, especially if you’re not really an SEO expert, is the screaming frog SEO spider tool & crawler software.
Not only is screaming frog the least complicated among all the tools we’ve used, it also gives accurate results and it’s easy to understand and navigate. And the best part? It’s completely free.
Let me walk you through the basics of what you need to know about screaming frog. Refer to the image below:
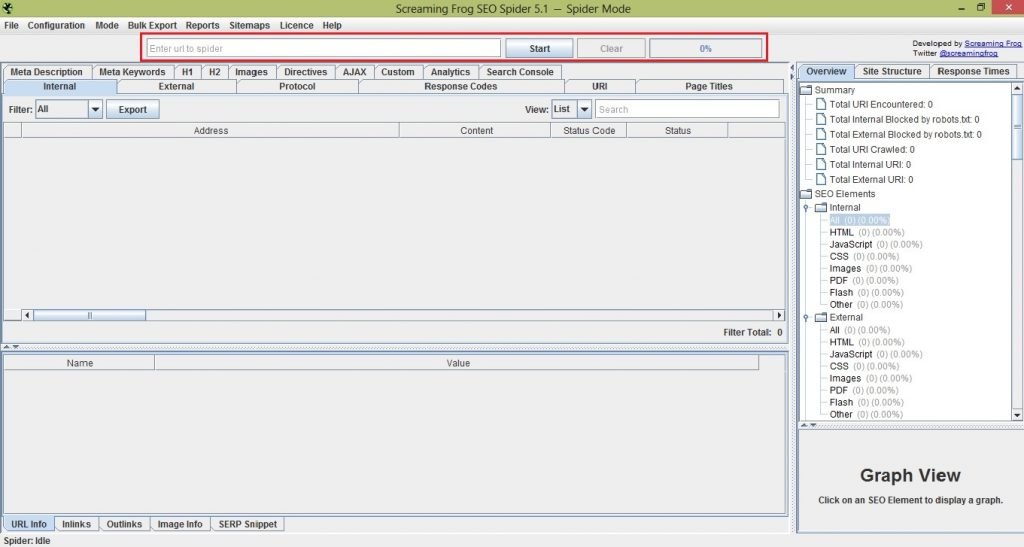
After you install the tool, this is the first thing you’ll see. To check your website, all you have to do is place the URL of your page in the search bar seen at the uppermost part of the window. Once you start the process you’ll also see the total percentage crawled.
Since we are discussing duplicate content, let me show you the parts of this tool that concerns that issue. Below I’ve boxed the area you should focus on when looking for content duplication.
You should also remember to select ‘duplicate’ on the filter option so that the tool will generate results that would display all the page in your website with duplicate content.
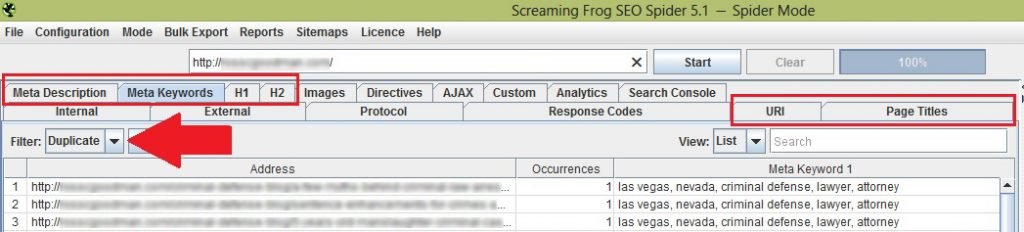
You only need to focus on six things: Meta description, Meta keywords, H1, H2, URI and Page titles. As seen in the image above, the results are displayed below these tabs.
Aside from this, you can also view the results on the right most part of the window. See image below:
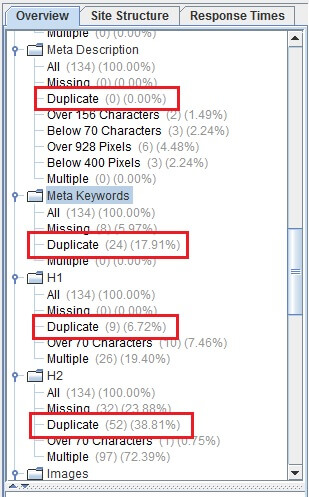
Here, you can see an overview of the results including the total number and percentage of duplicated content.
Simple, right? One thing about screaming frog is that you can only use it to determine the issues present in your website. This means you won’t be able to alter anything in your page using this tool. So it’s either you address the issues in the CMS your website has (that’s if it allows it) or you use another tool where you can apply the fixes – like Google Webmasters Tool.
There’s really nothing to be afraid of about duplicate content. It happens. People from Google already said so that the content present on the internet comprises 25-30% of duplicated content – and that’s okay! It’s inevitable. Just remember not to come off as if you’re trying to unethically manipulate results.
Even if applying the fixes to this issue may take a bit of time, anything done in the right way is always worth it in the long run. By doing this, your website may be able to give you a better spot on the Google search results page as well as a bigger ROI.